From chronic skin conditions to early skin cancer detection, medical dermatology focuses on diagnosing and treating disorders that affect skin, hair, and nails. Effective care starts with our experienced providers and a clear, evidence-based approach.
What Is Medical Dermatology?
Medical dermatology is the branch of dermatology focused on diagnosing and treating skin, hair, and nail conditions that affect health and quality of life. Treatment is guided by patient history, physical exam, diagnostic tools, and response to therapy. Common conditions addressed through medical dermatology include the following:
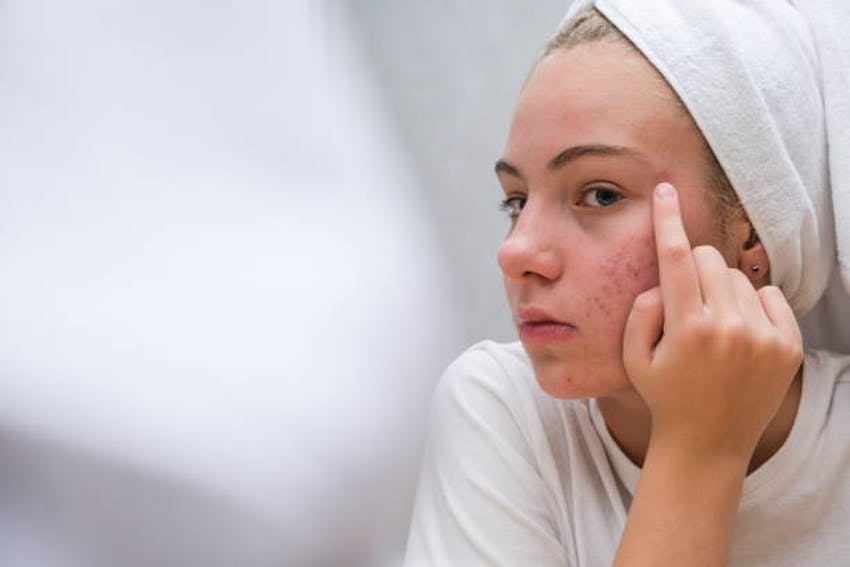
- Acne – An Inflammatory condition triggered by clogged pores and bacteria
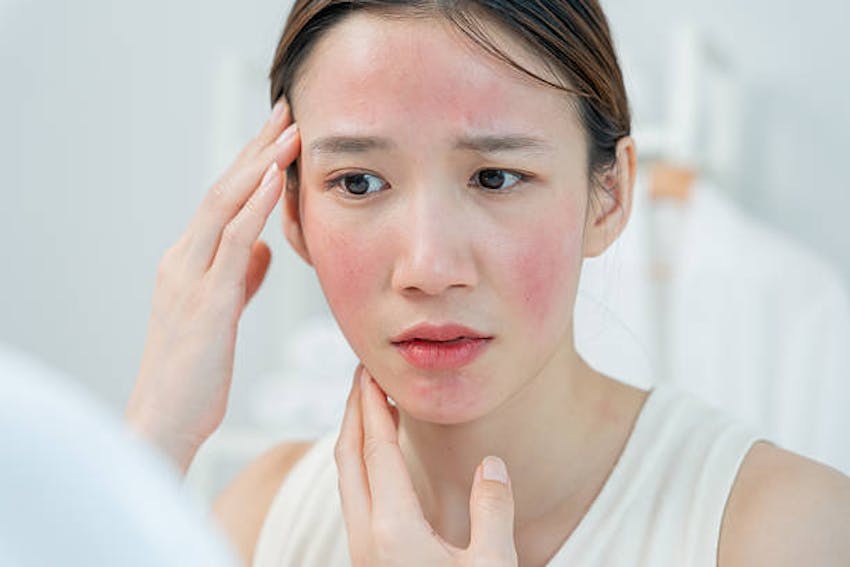
- Rosacea – Chronic facial redness, bumps, and flare-ups
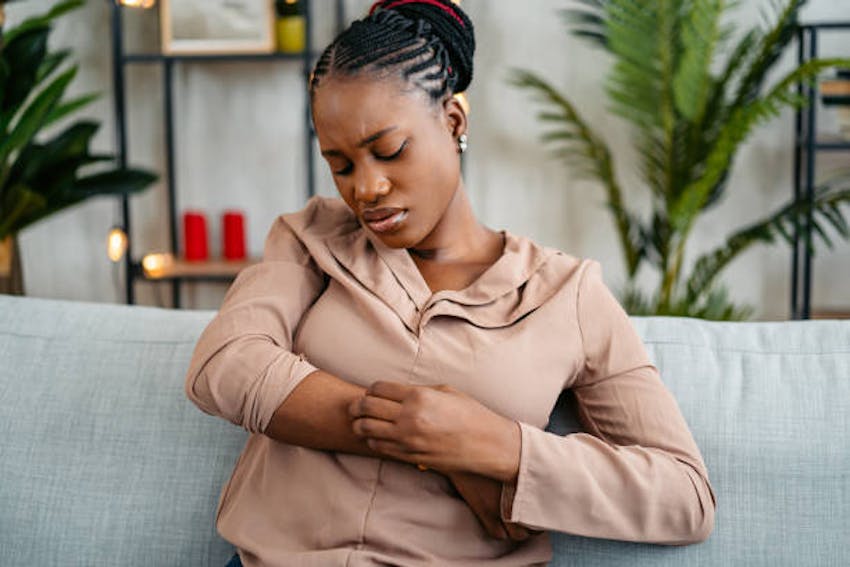
- Eczema & Dermatitis – Itchy, irritated, and inflamed skin
- Psoriasis – Immune-mediated plaques and skin thickening
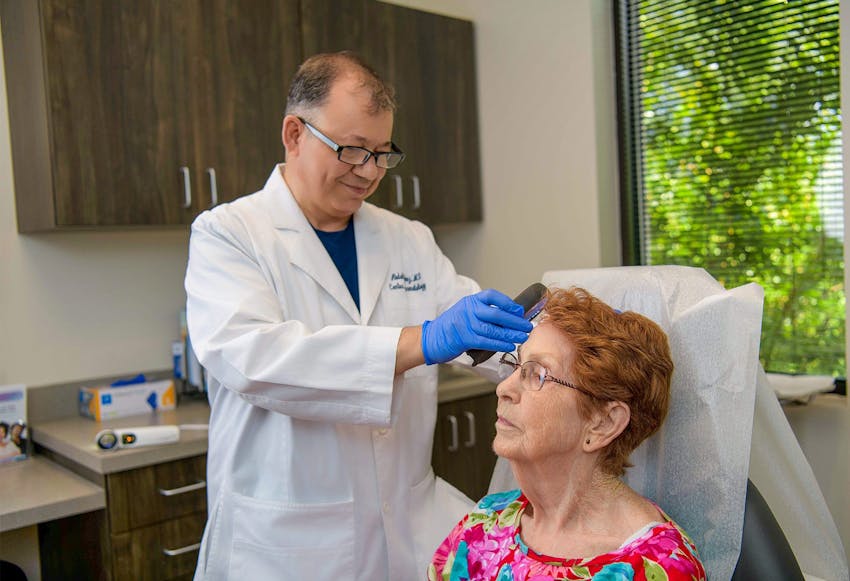
- Skin Cancer – Including basal cell, squamous cell, and melanoma
- Hair Loss – Including alopecia and hormonal hair thinning
- Scars & Keloids – Raised or depressed lesions from injury or acne
- Moles & Growths – Skin checks for atypical nevi or benign lesions
- Rashes – Evaluation of persistent or unexplained eruptions
- Warts & Molluscum – Viral lesions of the skin
- Pediatric Skin Conditions – Rashes, eczema, warts, and more